When buying and using essential oils you may come across the word chemotype or see something like this:
Rosemary ct. camphor or the botanical name of Rosemarinus officinalis ct. camphor
The ct. abbreviation means "chemotype". In this example, "ct. camphor" refers to the chemotype of rosemary, which contains high levels of camphor. You may also see it simply written Rosemary Camphor.
After reading this quick guide on essential oil chemotypes you will have a greater understanding of what they are and why they are important to aromatherapy.

What are Essential Oil Chemotypes?
"Chemotype" means a different chemical type.
Chemotypes are plants of the same genus and species which look identical but have a variation in the chemical components of their essential oils due to different conditions of growth. The listed chemotype is the oil’s overriding constituent.
Not all plants produce chemotypes, but some have the genetic ability to produce different chemical constituents based on environmental factors.
Here are a few environmental factors that may produce different chemotypes:
- Climate
- Growing elevation of plant
- Growing condition of plant
For example, in Basil Linalool, there is a high linalool count present. Here is a GC/MS from Plant Therapy:
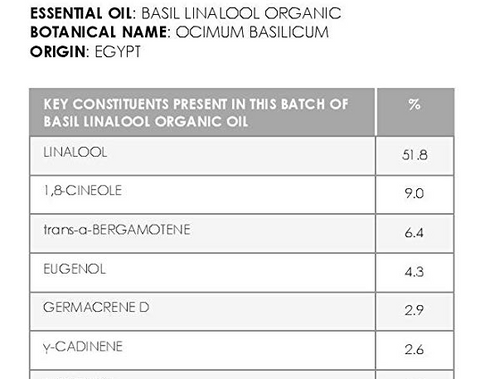
You see that the constituent linalool is at 51.8%. That is the main component of this basil essential oil, and that is why it is listed as Basil Linalool:
Why Essential Oil Chemotypes Matter?
Chemotypes of essential oil are the varieties that come from the same plant but have different chemical compositions. Knowing the chemotype of your oil can help you choose the right essential oil for your purpose.
When it comes to essential oils, different chemotypes will have different therapeutic properties, aromas, and even safety concerns.
How to Determine the Chemotype
Be aware that not all essential oil companies will identify the chemotype of the essential oil on the label. If it is an essential oil that you know has chemotypes, then you can look at the testing done on the oil to see what chemical component has the highest percentage.
Like the example above of the GC/MS test from Plant Therapy, it shows that linalool has the highest percentage. So you know that chemotype is linalool and that your essential oil is rich in the chemical component of linalool.
Essential Oil Chemotype Examples
Doterra® Thyme bottle label does not differentiate what chemotype it is, but when looking at the main chemical components, they list Thymol. So you can conclude that they offer Thymus vulgaris ct. thymol.
Most Common Essential Oil Chemotypes
When looking at the essential oil chemotypes, the botanical names will be the same but the ct. will highlight the main chemical component the oil is made of.
Remember I mentioned that not all plants produce chemotypes, here are the common ones you will more than likely come across.
Essential Oil | Chemotypes |
| Thyme |
|
| Rosemary |
|
| Sage |
|
| Basil |
|
While this is not an exhaustive list, it is the most common essential oil chemotypes you will come across for aromatherapy.

Final Thoughts on Chemotypes of Essential Oils
Chemotypes are the chemical makeup of an essential oil. Chemotypes of an essential oil can be determined by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS). This process will identify the compounds in an essential oil and the ratios of these compounds. The ratio of these compounds is what determines the chemotype.
Chemotypes are important because they can determine the therapeutic properties of an essential oil. For example, two oils that come from the same plant can have different chemotypes and different effects on the body. One oil may be calming while the other is invigorating.
It is important to know the chemotype of an essential oil before using it for aromatherapy or any other purpose. It's important to choose the right chemotype for your needs, as each one can provide different benefits. When selecting an essential oil, be sure to check the label for information on the specific chemotype. This will help you choose the oil that's right for you.
What is a therapeutic grade essential oil?
Therapeutic grade is simply a marketing term that any company can claim. No government agency or organization “grades” or “certifies” essential oils in the United States.
Share on Pinterest






